Overview of Dapr on Kubernetes
Dapr on Kubernetes
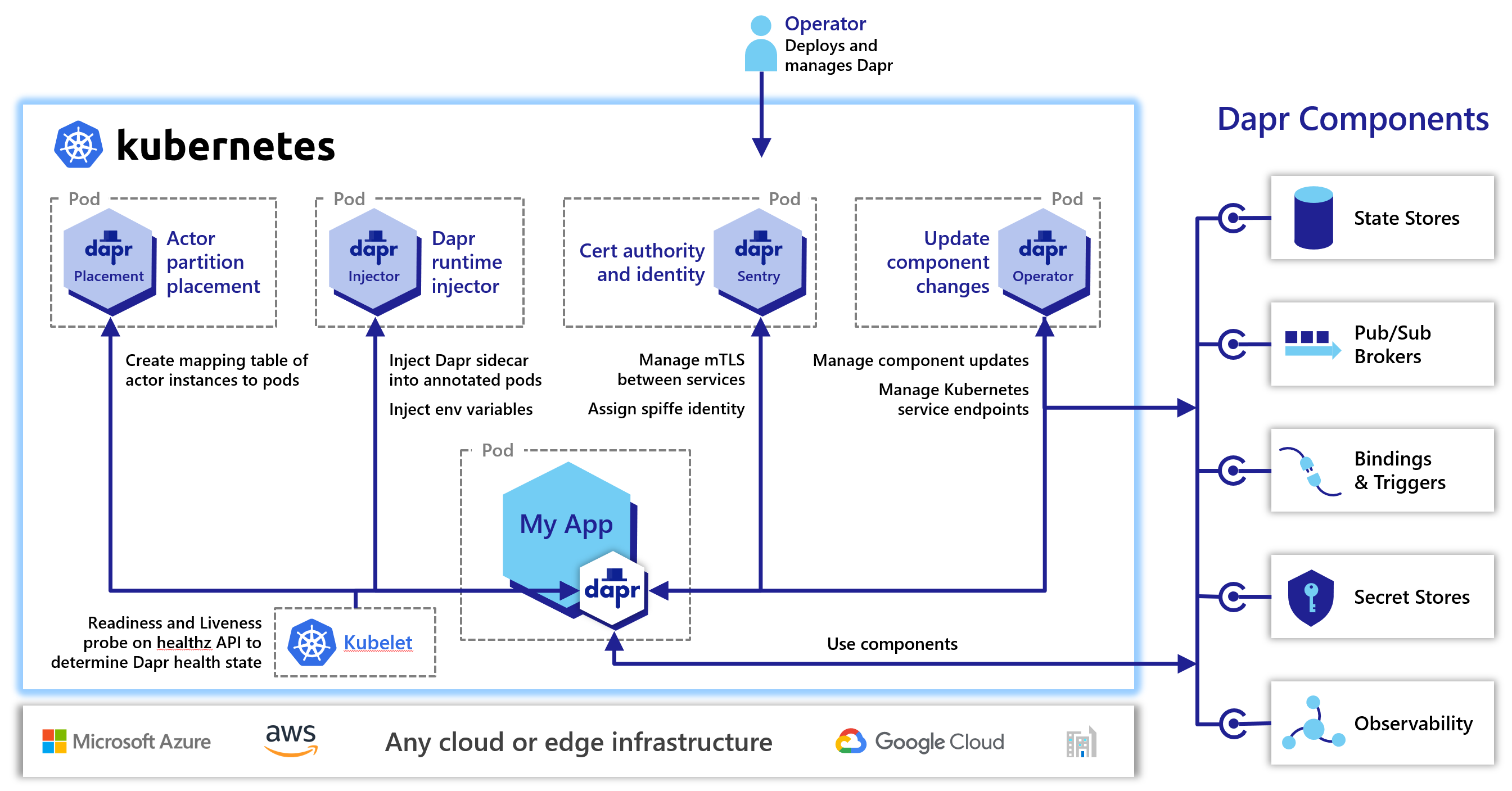
Dapr can be configured to run on any supported versions of Kubernetes. To achieve this, Dapr begins by deploying the dapr-sidecar-injector, dapr-operator, dapr-placement, and dapr-sentry Kubernetes services. These provide first-class integration to make running applications with Dapr easy.
- dapr-operator: Manages component updates and Kubernetes services endpoints for Dapr (state stores, pub/subs, etc.)
- dapr-sidecar-injector: Injects Dapr into annotated deployment pods and adds the environment variables
DAPR_HTTP_PORTandDAPR_GRPC_PORTto enable user-defined applications to easily communicate with Dapr without hard-coding Dapr port values. - dapr-placement: Used for actors only. Creates mapping tables that map actor instances to pods
- dapr-sentry: Manages mTLS between services and acts as a certificate authority. For more information read the security overview.
Deploying Dapr to a Kubernetes cluster
Read this guide to learn how to deploy Dapr to your Kubernetes cluster.
Adding Dapr to a Kubernetes deployment
Deploying and running a Dapr enabled application into your Kubernetes cluster is as simple as adding a few annotations to the deployment schemes. To give your service an id and port known to Dapr, turn on tracing through configuration and launch the Dapr sidecar container, you annotate your Kubernetes deployment like this. For more information check dapr annotations
annotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/app-id: "nodeapp"
dapr.io/app-port: "3000"
dapr.io/config: "tracing"
Quickstart
You can see some examples here in the Kubernetes getting started quickstart.
Supported versions
Dapr is tested and supported on the following versions of Kubernetes.
| Supported Kubernetes versions |
|---|
| 1.17.x and above |
Related links
- Deploy Dapr to a Kubernetes cluster
- Upgrade Dapr on a Kubernetes cluster
- Production guidelines for Dapr on Kubernetes
- Dapr Kubernetes Quickstart